Infrared Thermometer: Here’s What You Must Know
John Souffront
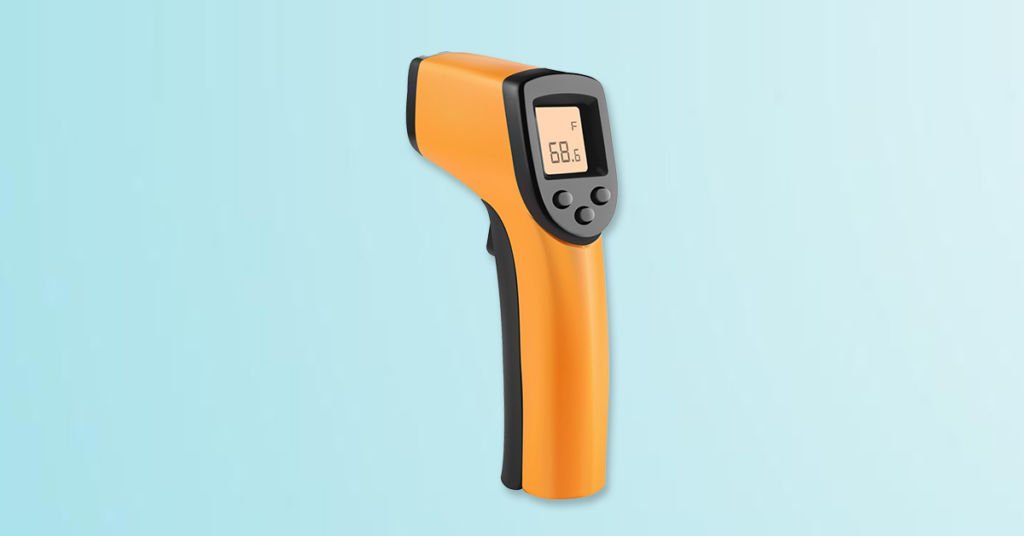

An Introduction to Infrared Thermometer
An infrared thermometer (also referred to as a non contact thermometer) is a device that monitors a subject’s surface temperature by analyzing its thermal radiation levels.
In industrial settings, as well as during a number of situations, IR thermometers are more prevalent because it might be risky or difficult to measure temperature directly from a subject. In order to measure temperature remotely, these gadgets make use of a phenomenon called thermal radiation.
Thermal radiation is produced by almost every object. The IR thermometer gauges temperature by directing a body’s infrared radiation toward a spot known as a thermopile. Electric current flowing through the thermopile changes as it warms up. We obtain the temperature reading based on the current that the thermopile produces.
IR thermometers, also known as distance-to-spot-ratio thermometers, have a range of temperature measurements depending on how they get built. 4:1, 8:1, 30:1, and even 50:1 are the standard distance-to-spot ratios. The greater the ratio, the greater the distance you can elude the heat source.
An infrared thermometer range covers -100°F to 10000°F temperature, making it convenient to inspect most objects, and at various temperature levels.
If you are looking for the best infrared thermometer, this blog will definitely help you decide upon one because we will also discuss three popular infrared thermometer types.
Let’s understand how infrared thermometers work.
You might also want to read: Infrared Thermography: An Exclusive Guide That You’ll Need (2022)
How Does an Infrared Thermometer Work?
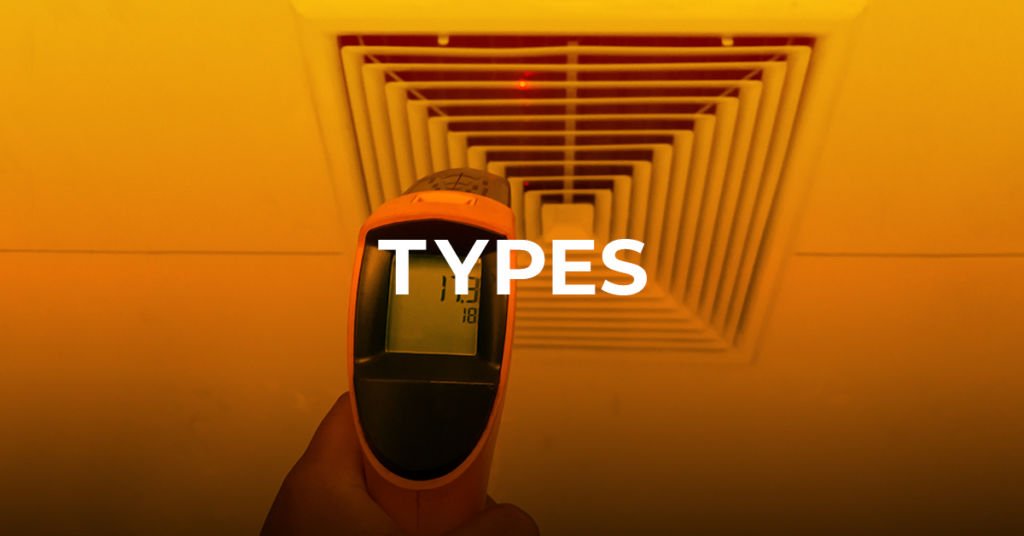
In order to measure the temperature of a wall or other object, the infrared thermometer contains a laser that makes it easier to point the thermometer to a specific spot.
The temperature in units is shown on the gadget once the laser measures the temperature the wall or other surface emits.
When checking the temperature of objects or regions that can get very hot, such as a car engine or a Thanksgiving turkey, the capacity to read the temperature of an area remotely is useful.
Infrared thermometers come in a variety of designs, but they all operate on the same fundamental principles.
The infrared thermometer is a handheld pistol with a point-and-click interface that helps get an instant temperature reading from any non-organic surface, such as in the case of food, vehicles, or insulation.
The laser from an infrared thermometer marks the spot that needs measurement for temperatur. You can designate the center of the object whose temperature you wish to measure with the laser.
The entire area is greater than the laser, which is just a mark to indicate where you want to take a measurement.
Infrared thermometer accuracy holds good for most objects. However, reading infrared radiation from reflecting surfaces can make taking a measurement more challenging. As a result, they are more emissive on glossier surfaces.
Therefore, taking many readings from the same position and the area around the center point is essential if you want precise measurements.
You might also want to read: When and Why Should You Go For An Infrared Thermography Inspection
Popular Infrared Thermometer Types You Must Know About
In its simplest form, an infrared thermometer is made up of a lens that directs heat infrared radiation onto a detector, which converts it into a signal with a color code.
Since they don’t require direct touch with the measured object, infrared thermometers may monitor temperature at a distance.
However, the infrared thermometers available today can be configured in several different ways, depending on the task.
The following are the three most popular types of IR thermometers to know about.
Spot infrared thermometers
Often referred to as pyrometers, these thermometers help find and gauge the temperature at a particular spot on a surface. They resemble handheld radar guns. The use of spot infrared thermometers is a preference whenever thermal radiation needs measurement on assets that are difficult to access or on assets that are working in harsh environments.
It’s possible that you’ve seen heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) specialists in your office building or home utilizing a spot infrared thermometer to monitor the temperature of a ventilation system. They do this by pointing the gun toward the ceiling vents to get an accurate reading.
Spot infrared thermometers for preventive maintenance are help in situations like belt and bearing examination, electrical room monitoring, energy audits to find heat loss, fluid-handling systems, and many more.
The FOV and distance-to-spot ratio are the two primary metrics by which spot infrared thermometers measure temperature (D:S). A spot thermometer must have its target entirely inside its field of view to acquire an accurate temperature reading. Don’t forget about the ratio of distance to spot size; if the ambient temperature deviates from the desired value, an error will result.
Simply said, the distance-to-spot ratio is the diameter of the temperature measurement area divided by the distance to the object being measured. Higher ratios indicate higher resolution and fewer measurable areas for an instrument. For instance, a spot thermometer with a 40-to-1 ratio provides more precise results when measuring a small object than a 10-to-1 ratio device.
Infrared scanner systems
These infrared thermometers have a wider field of view and find widespread application in factories that utilize conveyors or web systems. Infrared scanner systems are come in handy for applications such as scanning products moving along a conveyor belt, sheets of glass, or metal emerging from an oven.
Infrared thermal-imaging cameras
In order to create two-dimensional thermographic images, thermal-imaging cameras, a more sophisticated form of radiation thermometer, measure temperature at numerous locations spread across a vast region.
Compared to a spot thermometer, thermal imaging cameras rely significantly more on software and hardware.
Most cameras can connect to specific software and display real-time images for a more thorough analysis, accuracy, and report generation.
In addition, modern handheld thermal imaging cameras are portable.
Infrared thermal imaging cameras allow users to switch between different color palettes to distinguish manifold temperature variations.
- Iron palette: It is the most popular palette. Black represents the coldest places, blue or purple the slightly hotter areas, red, orange, or yellow the mid-range temperatures, and white the hottest areas.
- Black and white color palette: Also known as grayscale, this color scheme visually exposes details by merely displaying black-to-white hues moving through various shades of gray. Grayscale is most frequently used in security cameras or night vision. Due to the difficulty of identifying temperature variation using only two colors, it is rarely employed in machinery imaging.
- Rainbow palette: By using a variety of colors to represent temperature changes, the rainbow palette best illustrates thermal sensitivity. The rainbow palette employs additional colors to denote a broader range of temperatures, much like the iron palette.
Other Features
Infrared cameras have other capabilities, such as color alert, split-screen mode, and fusion mixing.
The color alarm feature allows you to define a temperature threshold above or below which the camera will not display a thermal image in color.
Fusion blending enables you to combine a conventional digital image with a thermal image’s lowest or highest average temperature.
There are many exciting things to learn from a thermal-imaging camera’s settings, but it’s easy for them to sidetrack professionals.
To that end, what features should one seek in a thermal-imaging camera? Heat sensitivity and detector resolution are the two most crucial characteristics to consider.
The detector resolution indicates how many pixels are visible in your photographs. The three most frequent resolutions, 160×120, 320×240, and 640×480, should all be supported by your camera. Images consisting of 307,200 pixels are displayed on a 640×480 imager.
Heat sensitivity is the minimum temperature difference a thermal imaging camera can detect. For example, suppose a camera claims to be sensitive to temperature differences of 0.05 degrees, for instance. In that case, it can detect a variation in surface temperature of only five-hundredths a degree.
Think about the lowest and highest temperatures that the thermal-imaging camera can capture. Typically, temperatures fluctuate from minus 4 degrees to over 2,200 degrees.
You might also want to read: Get An Infrared Thermography Inspection To Save Up to $11,000 In Repairs: Here’s How
Importance of a Good Quality Infrared Thermometer
Speedy Measuring
An infrared model is your best bet if you’re looking for a thermometer that gives you precise readings in a shorter time. Do not waste your money on a thermometer that takes too long to get reliable results. Infrared thermometers are ideal in this situation since they can give you a reading in a matter of seconds. Standard thermometers take longer to get an accurate reading than their digital counterparts.
Measurement From a Distance is Possible
These thermometers can collect readings from a considerable distance away without physically touching the subject. Unlike conventional thermometers, an infrared thermometer can be directed towards the target to take a temperature reading. Direct skin-to-skin contact is not required, unlike with conventional thermometers. Infrared thermometers are an excellent choice in the medical field to avoid contact with potentially infectious patients or equipment. This thermometer is perfect for the job if you need to take readings from extremely hot surfaces.
Measurement of Moving Parts is Possible
One more factor contributes to infrared thermometers’ widespread adoption. They can capture readings while the object is in motion, a feature that will come in handy when inspecting moving gear. Because of this function, users may keep a close eye on the machinery even as it’s being used. This is one of the most prominent of the thermometer’s many advantages.
Presence of Memory Function
Infrared thermometers have become increasingly common in recent years, and the vast majority now feature a memory function. This function allows multiple data points to be saved at once. Because of this fantastic feature, taking careful notes of dimensions is unnecessary. In contrast to utilizing pen and paper, this is a much more dependable and hassle-free option.
Compact, Rapidly Deployable, and More Powerful Than Ever
These infrared thermometers are pretty robust, even considering their cutting-edge technology. It’s easy to carry one of these thermometers around in your pocket because it is light and compact. The thermometer is small and lightweight, so you can take it wherever you go.
Final Words
This was an in-depth guide about IR thermometers and the underlying knowledge that one must have before going for an infrared thermography inspection.
If you have successfully read through till the end, you have enough knowledge to employ the right infrared thermographer, not fall for people claiming to be professionals but having little to no knowledge about the complex details.
However, you must look into the bigger picture. At present, apart from a thermography inspection, it is highly crucial to get a 40 year recertification done for your property to keep it safe from any internal and external damages that can be severe.
So, it’s best to employ experts at both of these services because you get these done at a lower cost when you get them done through a single individual. Additionally, you don’t have to deal with multiple people when you have that one person doing all the jobs.
This is where Souffront Construction and Engineering comes in. Being certified experts in property services like 40 year inspection, infrared thermography inspection, and concrete restoration, we are a strong team of general contractors, structural engineers, Level II certified infrared thermographers and recertification experts.
Feel free to contact our support team for your thermography inspection needs and queries.
John Souffront
John Souffront is a seasoned leader in the construction and engineering industry, with over a decade of experience at the helm of Souffront Construction & Engineering. Known for his unwavering commitment to excellence and innovation, John has propelled his firm to the forefront of the field, delivering cutting-edge solutions for complex projects around the country.
Build Your Project
Ensure safety and compliance on your construction site with our experienced team. Call us today.
Contact Us